Tutorial 05 - Acoustic Wave Propagation
Acoustic Forward Simulation
In this notebook we will go through a simple example of setting up a purely acoustic forward simulation in PestoSeis for a 2D portion of the “SEG/EAGE Salt and Overthrust Model” (Aminzadeh et al., 1997).
Preamble
[1]:
import pestoseis
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import h5py
from scipy.interpolate import RectBivariateSpline
Model Interpolation
First, we will import the HDF5 (.h5) model which contains the following keys:
vp: P-wave velocity model (in units of [m/s])ijsrcs: Indices of the source positionsijrecs: Indices of the receiver positions
[2]:
data_path = "model.h5"
with h5py.File(str(data_path), "r") as f:
vp = np.array(f["vp"])
sources = np.array(f["ijsrcs"], dtype=int)
receivers = np.array(f["ijrecs"], dtype=int)
We can plot the velocity model to verify that the data has been imported correctly.
[3]:
plt.figure(figsize=[10, 16])
im = plt.imshow(vp.T, origin="upper", cmap="jet")
plt.plot(sources[0, :], sources[1, :], "*r")
plt.plot(receivers[0, :], receivers[1, :], ".c")
plt.xlabel("x-Position")
plt.ylabel("z-Position")
plt.title("Overthrust P-Wave Velocity Model [m/s]")
plt.colorbar(im, fraction=0.046*(10/16), pad=0.04)
plt.show()
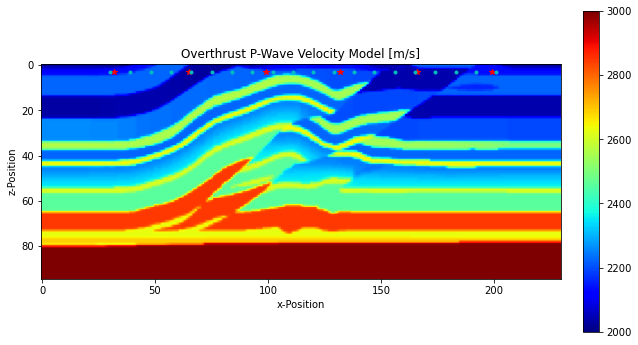
Notice that the P-wave velocity model is currently fairly coarse (ie. there are relatively few samples in the x- and z-directions). This discretisation is currently too coarse for the desired source frequency we want to use for this example (50 Hz), so we need to interpolate this coarser model onto a finer grid. A fairly simple way of accomplishing this is to use the RectBivariateSpline tool from the scipy package.
We can set a desired scaling factor (see scale) which will scale the number of samples in each of the x- and z-directions.
[4]:
scale = 2
interp_fun = RectBivariateSpline(np.linspace(0, vp.shape[0], vp.shape[0]), np.linspace(0, vp.shape[1], vp.shape[1]), vp)
vp = interp_fun(np.linspace(0, vp.shape[0], vp.shape[0]*scale), np.linspace(0, vp.shape[1], vp.shape[1]*scale))
sources *= scale
receivers *= scale
plt.figure(figsize=[10, 16])
plt.imshow(vp.T, origin="upper", cmap="jet")
plt.plot(sources[0, :], sources[1, :], "*r")
plt.plot(receivers[0, :], receivers[1, :], ".c")
plt.xlabel("x-Position")
plt.ylabel("z-Position")
plt.title("Overthrust P-Wave Velocity Model [m/s]")
plt.show()
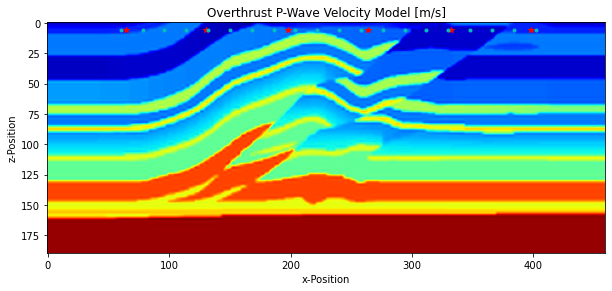
Simulation Setup
Next, we can set up the simulation itself. For this example, we will be explicitly defining the following:
Time step
Number of time steps
Source time function characteristics (Ricker wavelet)
Free surface boundary conditions at the surface of the domain
PMLs on all other sides
[5]:
# Temporal discretization
nt = 2000
dt = 0.0005
t = np.arange(0.0, nt*dt, dt)
# Spatial discretization
nx = vp.shape[0]
nz = vp.shape[1]
dh = 10 / scale
# Sources
t0 = 0.03
f0 = 25.0
ijsrc = sources[:, 2]
# Source time function
sourcetf = pestoseis.seismicwaves2d.sourcetimefuncs.rickersource( t, t0, f0 )
# Receivers
nrec = receivers.shape[1]
recpos = receivers.T * dh
print(("Receiver positions:\n{}".format(recpos)))
# Initiallize input parameter dictionary
inpar = {}
inpar["ntimesteps"] = nt
inpar["nx"] = nx
inpar["nz"] = nz
inpar["dt"] = dt
inpar["dh"] = dh
inpar["savesnapshot"] = True
inpar["snapevery"] = 50
inpar["freesurface"] = True
inpar["boundcond"] = "PML" #"GaussTap", "PML", "GaussTap","ReflBou"
Receiver positions:
[[ 300. 30.]
[ 390. 30.]
[ 480. 30.]
[ 570. 30.]
[ 660. 30.]
[ 750. 30.]
[ 840. 30.]
[ 930. 30.]
[1020. 30.]
[1110. 30.]
[1200. 30.]
[1290. 30.]
[1380. 30.]
[1470. 30.]
[1560. 30.]
[1650. 30.]
[1740. 30.]
[1830. 30.]
[1920. 30.]
[2010. 30.]]
Running the Simulation
Now that we have set up the forward simulation, we can run this using solveacoustic2D in pestoseis.
[6]:
seism, psave = pestoseis.seismicwaves2d.acousticwaveprop2D.solveacoustic2D(inpar, ijsrc, vp, sourcetf, f0, recpos)
Starting ACOUSTIC solver with CPML boundary condition.
Stability criterion, CFL number: 0.42734622684758544
* Free surface at the top *
Size of PML layers in grid points: 21 in x and 21 in z
Time step dt: 0.0005
Time step 1900 of 2000
Saved acoustic simulation and parameters to acoustic_snapshots.h5
Plotting the Results
[7]:
h5_data = "acoustic_snapshots.h5"
anim = pestoseis.seismicwaves2d.animatewaves.animateacousticwaves(h5_data, clipamplitude=0.1)
plt.close(anim._fig)
from IPython.display import HTML
HTML(anim.to_html5_video())
[7]:
References
Aminzadeh, F., Brac, J., Kunz, T., Society of Exploration Geophysicists, & European Association of Geophysicists and Engineers. (1997). 3-D salt and overthrust models. Society of Exploration Geophysicists. https://wiki.seg.org/wiki/SEG/EAGE_Salt_and_Overthrust_Models